Semi Solid dosages
Ointments are General/Topical pharmaceutical dosage forms those are manufactured by automatic process and semi automatic process.
Ointments along with similar products like creams, lotions, gels or pastes are certain formulations primarily designed to be applied to the skin. For along time now, they are being used for various medical and non-medical purposes. They are a vital part of the medication industry.
We have been using ointments as emollients, protectants, antiseptics, antipruritics, astringents, and keratolytics to name a few. In addition to their use on skin, some of the ointments are also used on mucous membranes of different organs like eyes, nose, anus or rectum.
I bet you have used these medicines multiple times in your life. Have you ever wondered how they are produced and filled in these small tubes? If your answer is yes, then this post is for you.
The purpose of this article is to take you through the process they use in the ointment manufacturing plants for the production of the ointments and filling them in tubes. So, let’s move to the procedure directly without wasting any time.
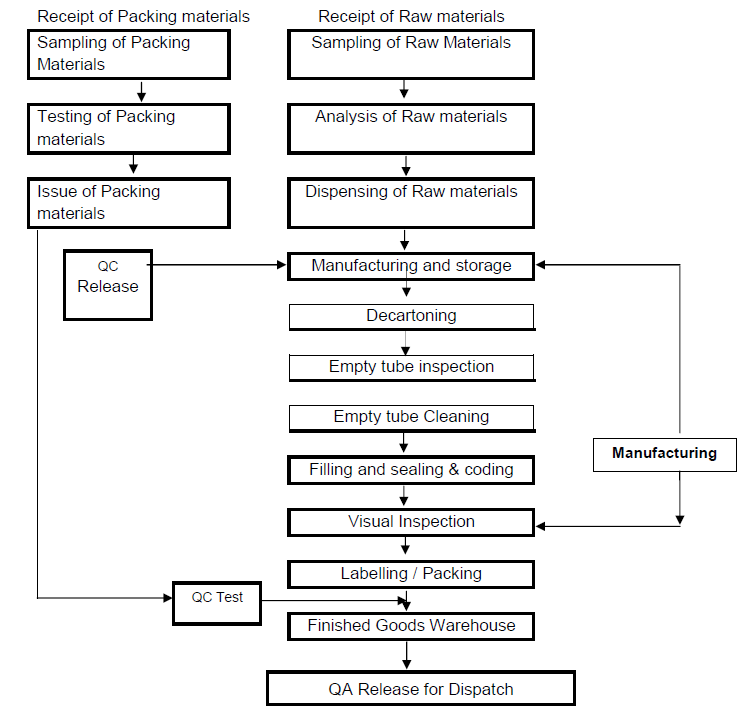
Manufacturing Procedure of Ointment:
The manufacturing procedure of ointment as same as that of cream, lotion, paste or gel. There are two processes used for the production of these formulations i.e. automatic process and semi-automatic process. Let’s discuss both of them one by one.
A. Automatic Process:
This process consists of the following steps:
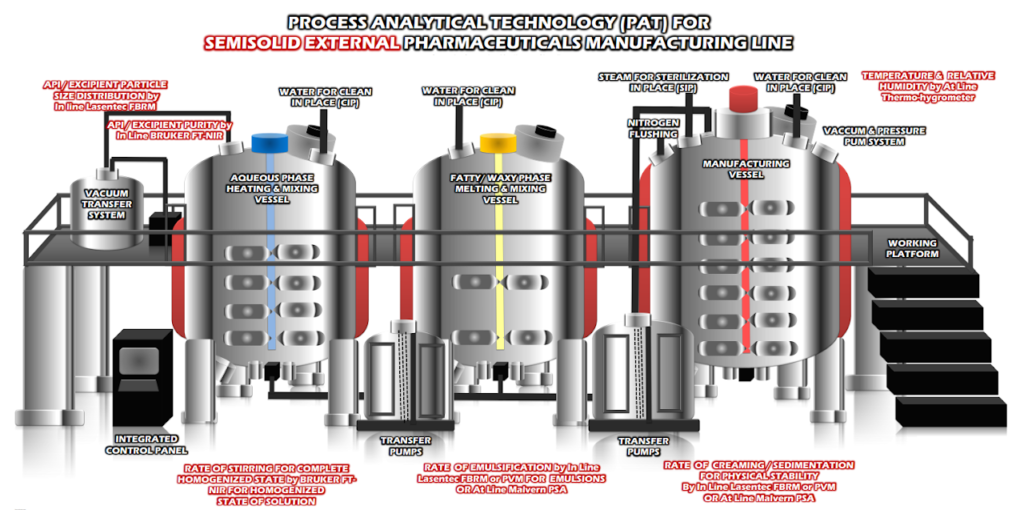
1. First of all, the water-soluble (aqueous phase) components are dissolved in demineralized (free from dissolved minerals) water. This process is called the water phase, and it is done in a particular container, known as the water phase vessel.
2. Similarly, the wax and oil components are mixed in another container, referred to as the wax phase vessel. It is called the wax phase.
3. Both these containers are heated and mixed thoroughly with the help of motor-driven agitators.
4. After this, all these components (i.e. the melted wax and heated water) are filtered and moved to another container through pipes with the help of vacuum system. This one is called the ointment manufacturing vessel. The drug component of the ointment (if left any) are added at this step while heating and stirring the mixture.
5. High-speed homogenizers and emulsifiers are also used for the homogenization and emulsification of the mixture to distribute the components as uniformly as possible.
6. When the product is ready, a bump pump is used to transfer it to the storage tank. The storage vessel usually has heating and moving facility(wheels).
7. The storage vessel is, then taken to the filling machine and the material is heated to make the transfer easy. Then a metering pump is used to transfer the product to the hopper of the filling machine.
8. Triple roller mill is used to remove the extra water from the final product before filling it into the tubes. It also helps further homogenizing the product.
9. The tubes are loaded into the filling machine. The piston of the filling machine cylinder sends out the calculated amount of the ointment take goes through a nozzle into the tube due to sucking mechanism.
10. After filling, the tube passes through the pressing station, crimping station and coding stations respectively.
11. In the case of plastic tubes, they first go to the air blowing station where hot air is blown at the end of every tube. In the end, there are sealing and trimming processes after which they are ejected out from the filling machine.
12. CIP (Clean-in-place) systems automatically wash all the containers used in the processes… and our ointment tubes are ready to hit the market.
B. Semi-Automatic Process:
This process consists of the following steps:
1. In this process, first water is heated in a container; then wax components are added in the same container. They are stirred and heated together. After that, the drug components are also introduced in the same container, and heating and stirring are continued. The planetary mixer is used to help the thorough mixing.
2. The material is transferred to the storage vessel passing through a colloid mill for the reduction of particle size as well as for the proper homogenization of the product. The storage vessel will have a heating system and wheels for movement.
3. the next procedure is same. The material is heated in the storage vessel to make sure easy transport to the filling machine. The metering pump is used for the transportation. Triple Roller Mill helps in removing extra liquid content from the final product.
4. The procedure for filling, sealing and packing the tubes is also the same as discussed before in the automatic process.